RIANT conducts design research for smart grids that are decarbonized, highly reliable, high-quality, and highly efficient next-generation network systems that utilize information and communications technology (ICT) to achieve carbon neutrality.
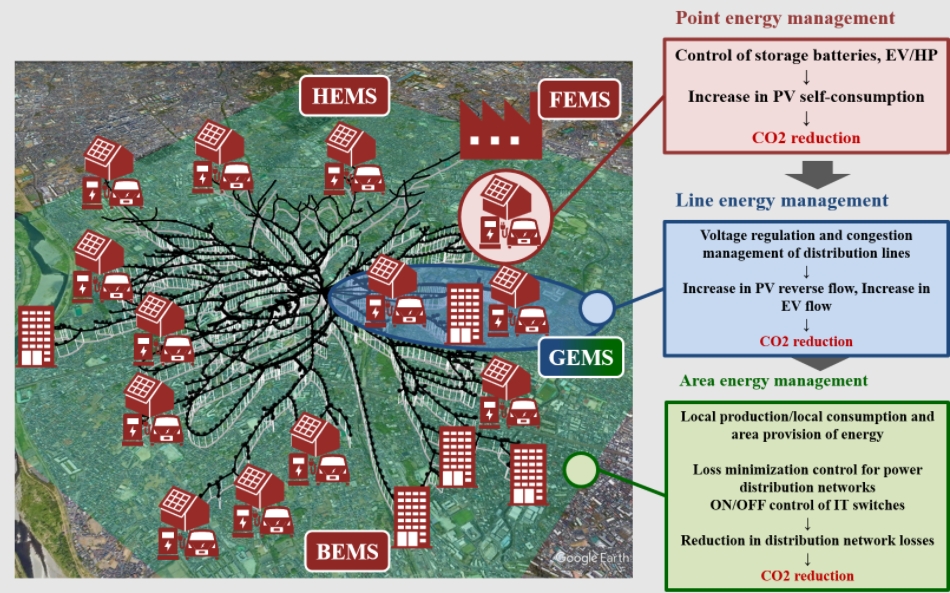
RIANT aims to establish an optimal cooperative system that harmonizes the planning, operation, and control of these three core areas: (1) Energy management of “points” that targets power users (point energy management), (2) Energy management of “lines” that targets the power transmission network (line energy management) and (3) Energy management of “area” that targets the region (area energy management)
RIANT aims to establish an optimal cooperative system that harmonizes the planning, operation, and control of these three core areas.
(1) Point energy management
The control target is the demand from storage batteries, EVs, heat pump water heaters, etc., in houses and buildings. RIANT researches methods to maximize the self-consumption of photovoltaic (PV) power without burdening power users’ life or business.
(2) Line energy management
The control targets are voltage regulation devices in transmission and distribution networks, and smart inverters, which are being studied in recent years. RIANT is researching methods to control voltages within permissive range and prevent congestion of distribution lines by using ICT to monitor power flows that change in complex ways according to the power consumption and the amount of power generated by renewable energy sources.
(3) Area energy management
RIANT researches methods to achieve optimization, with point and line energy management as basic elements that spread across the area and cooperate. The research is undertaken to optimize the provision of electric power in the entire region, maximize the ratio of local production for local consumption, and reduce CO2 emissions. RIANT is also researching how to model the elements that make up a certain geographical area and integrate and quantify these elements. For example, the efforts include linking electric power with transportation systems that are closely related to it, such as EVs, electric buses, light rail transit (LRT), and railways (sector coupling), and associating these vehicles with the flow of people, data on which can be utilized thanks to the spread of smartphones.
To pursue such research, RIANT is building an Energy Management System (EMS) platform that enables the modeling and various analyses of city-level network systems using satellite solar radiation data, grid data, and load demand data.